Shockwave IVL Overview & MOA
Discover the mechanism behind our proven crack record. Shockwave Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) simplifies the treatment of calcium via a unique mechanism of action (MOA) on an intuitive platform that’s low risk and consistently effective.

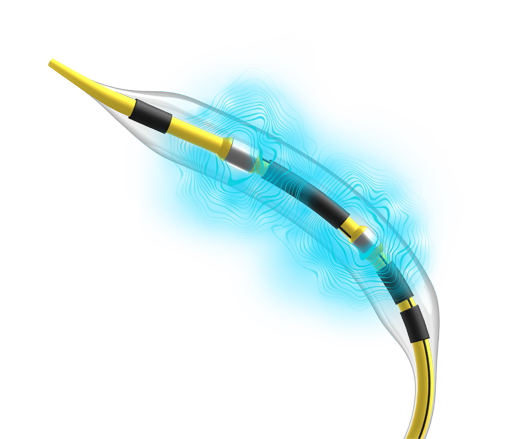
Not All Ultrasonic Acoustic Pressure Waves Are Created Equal: There’s Only One Shockwave
Adapted from the principles of urologic lithotripsy, Shockwave IVL uses ultrasonic acoustic pressure waves to modify calcified plaque in the cardiovascular system. But not every ultrasonic acoustic pressure wave is all it’s cracked up to be. We spent nearly a decade fine-tuning ours to create Shockwaves that maximize safety without tradeoffs for efficacy.
Shockwave is the only wavemaker with a published acoustic wave form1 and over 20,000 published patient outcomes across more than 500 journal articles.2
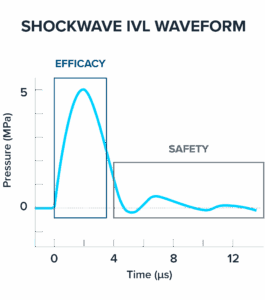
- Efficacy: driven by instantaneous, high-amplitude positive peak pressure to maximize compressive stress for calcium modification
- Safety: facilitated through an extended duration (low amplitude) negative peak pressure minimizing soft tissue damage due to tensile strength
Safety is Our DNA, And MOA.
From our early egg-cracking experiments that fractured hard shells but preserved soft membranes to treating more than one million patients worldwide today, Shockwave IVL has sparked a new era of first-in-class safety for the treatment of calcified arterial disease.
Statistics Callout
This section presents key statistical information with numbers and descriptions.
-
1million+Patients treated
-
20,000+Patient outcomes published
-
500+Journal articles published validating the safety & efficacy of IVL
-
The first prospective, female-only study of coronary interventions in complex calcific disease, in collaboration with female leaders.Coronary IVL
-
The largest-ever randomized clinical study of Shockwave peripheral IVL treatment in severely calcified peripheral lesions, out to 24 months.Peripheral IVL
-
Global prospective, multi-center, single-arm study assessing the safety and effectiveness of Shockwave peripheral IVL in treating long, calcified BTK lesions.Peripheral IVL
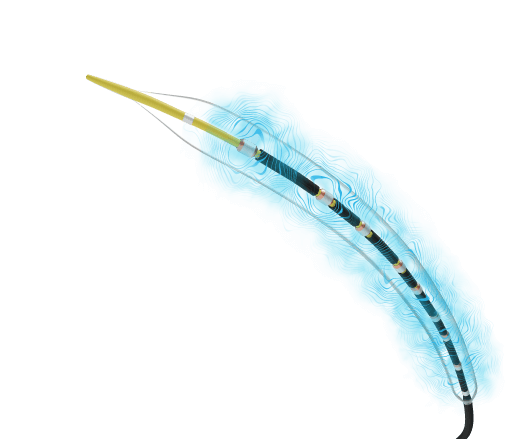
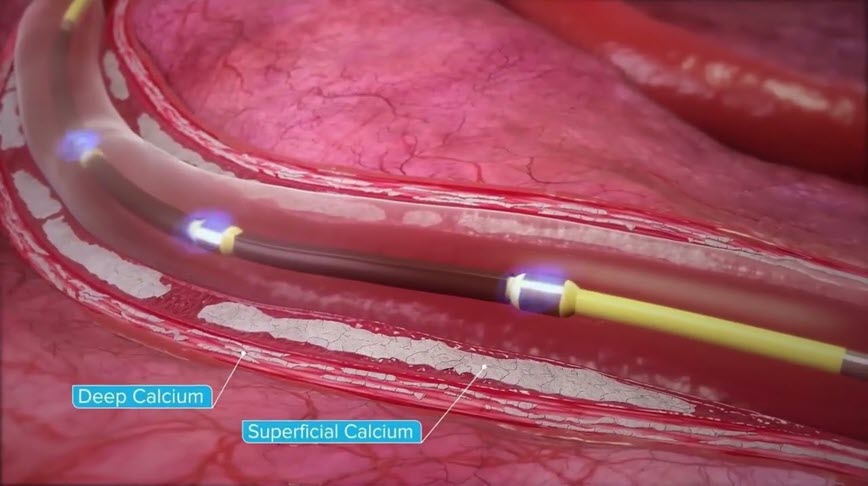
How Shockwave IVL Works
Shockwave IVL is an interventional procedure that utilizes a fluid-filled catheter connected to an energy source that generates mechanistically tuned ultrasonic acoustic pressure waves – or Shockwaves – for modification, fracture, and fragmentation of vascular calcification.
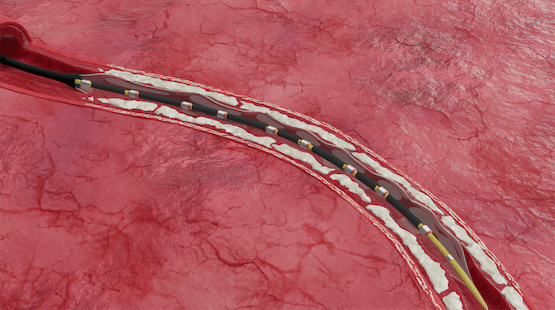
- The Shockwave IVL catheter is delivered to a calcified blockage in the artery and is inflated at low, subnominal pressures
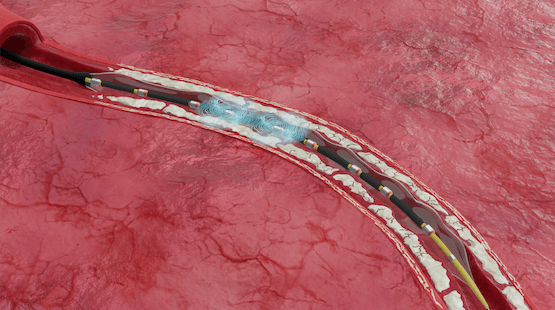
- Energy travels from the Shockwave generator to the fluid-filled balloon where it is rapidly absorbed
- The rapid energy absorption creates Shockwaves that propagate away from its origins and impact the calcified blockage while leaving soft, healthy tissue undisturbed
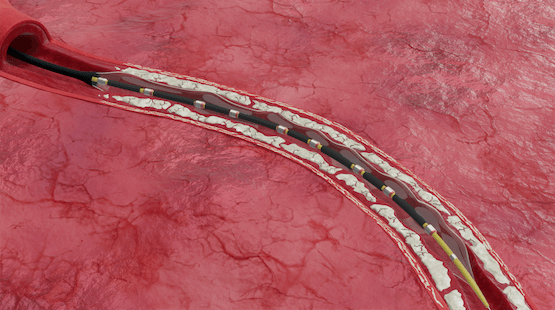
- Shockwaves modify, fracture and fragment the calcified blockage, improving arterial compliance and enabling optimal lumen expansion
-

Position & inflate
Catheter is delivered to a calcified blockage & inflated at low pressure -

Deliver Shockwaves
Energy travels from the generator to the fluid-filled balloon & is rapidly absorbed to create Shockwaves -

Improve arterial compliance
Shockwaves fragment the calcified blockage, improving arterial compliance & enabling optimal lumen expansion
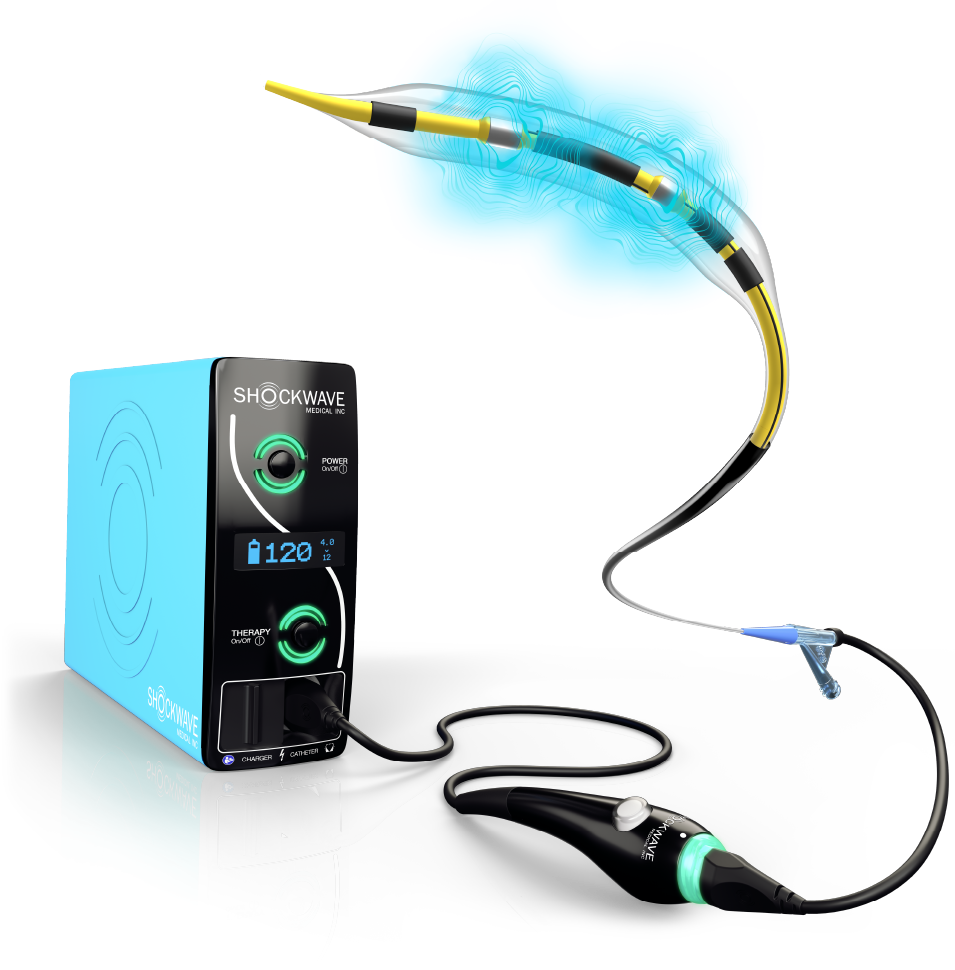
Simple and Intuitive System Set Up

Our Disruptive Devices
Explore our portfolio for treatment options from the heart to above and below the knee to find the right solution to help your next patient.
1: Kereiakes, D, Virmani, R, Hokama, J. et al. Principles of Intravascular Lithotripsy for Calcific Plaque Modification. Figure 1E. J Am Coll Cardiol Intv. 2021 Jun, 14 (12) 1275-1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2021.03.036.
2: Data on File at Shockwave Medical. Bibliography available upon request.