Shockwave IVL & Nodular Calcium
Shockwave Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) modifies both superficial and deep calcium without concerns about lumen size or hydrostatic force.¹
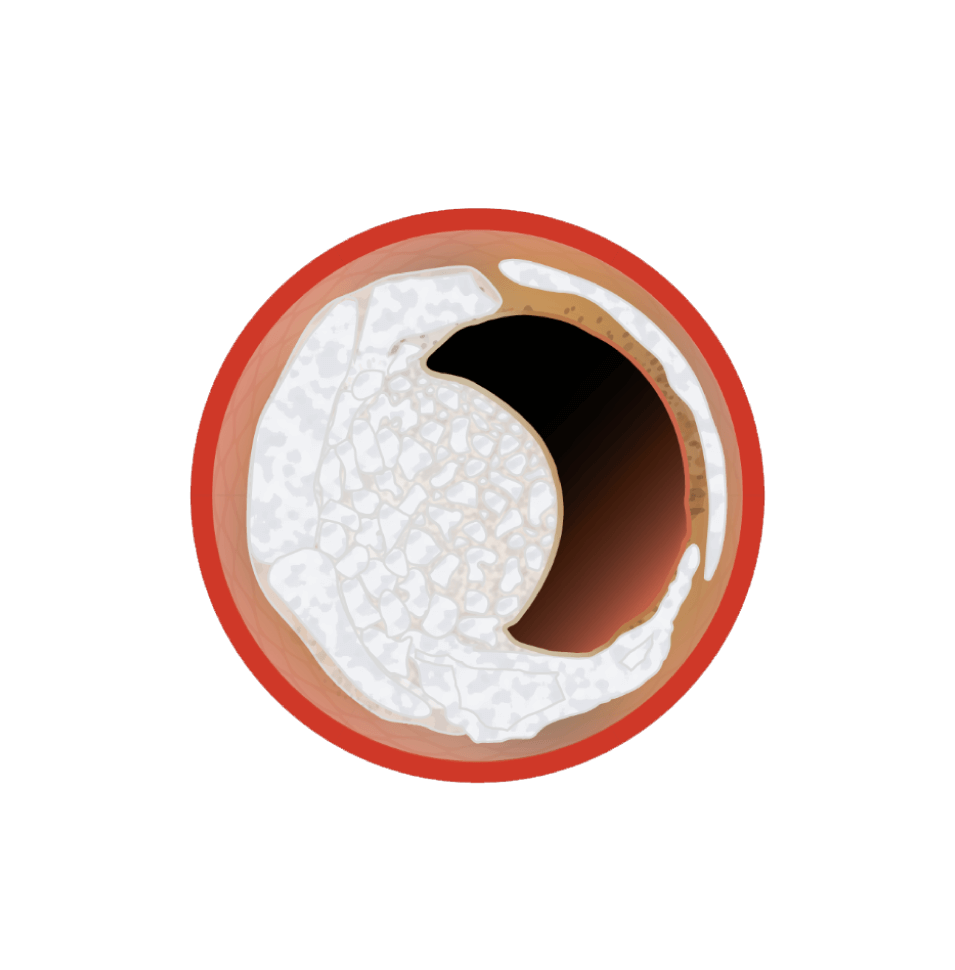
Definition and Pathologies of Calcific Nodules
Presenting as an eruptive calcium protrusion into the lumen, calcified nodules:
- Occur at sites of increased torsional stress2
- Have a higher prevalence of necrotic core calcium compared to adjacent regions3
- Are flanked proximally and distally by hard, collagen-rich calcium4
- Are believed to result from fragmentation of plates or sheets of calcium5
1: Kereiakes et al. Principles of Intravascular Lithotripsy for calcific plaque modification. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, 14(12), 1275-1292. (2021). doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2021.03.036
2: Mori H, et al. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Jan;11(1):127-142.
3: Torii S, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 Apr 6;77(13):1599-1611.
4: Virmani R, et al. Arterioscler Thrombosis Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1262-1275.
5: Designed in Partnership with Optima and VP Education.
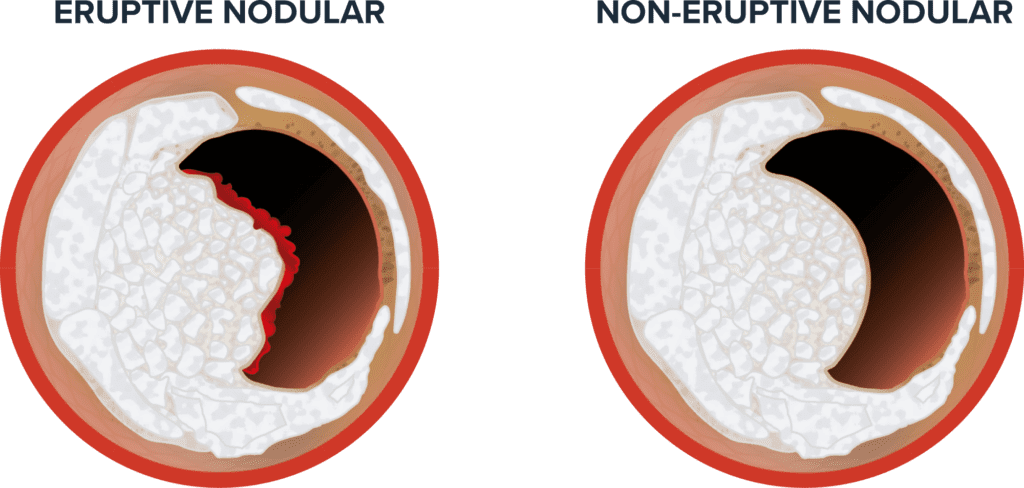
Within calcified nodules, there are two histological types:
- Eruptive nodular: Small dense fragments or nodules of calcium with a fibrous cap disruption and luminal thrombus
- Non-eruptive nodular: Small dense fragments or nodules of calcium with a smooth, intact fibrous cap
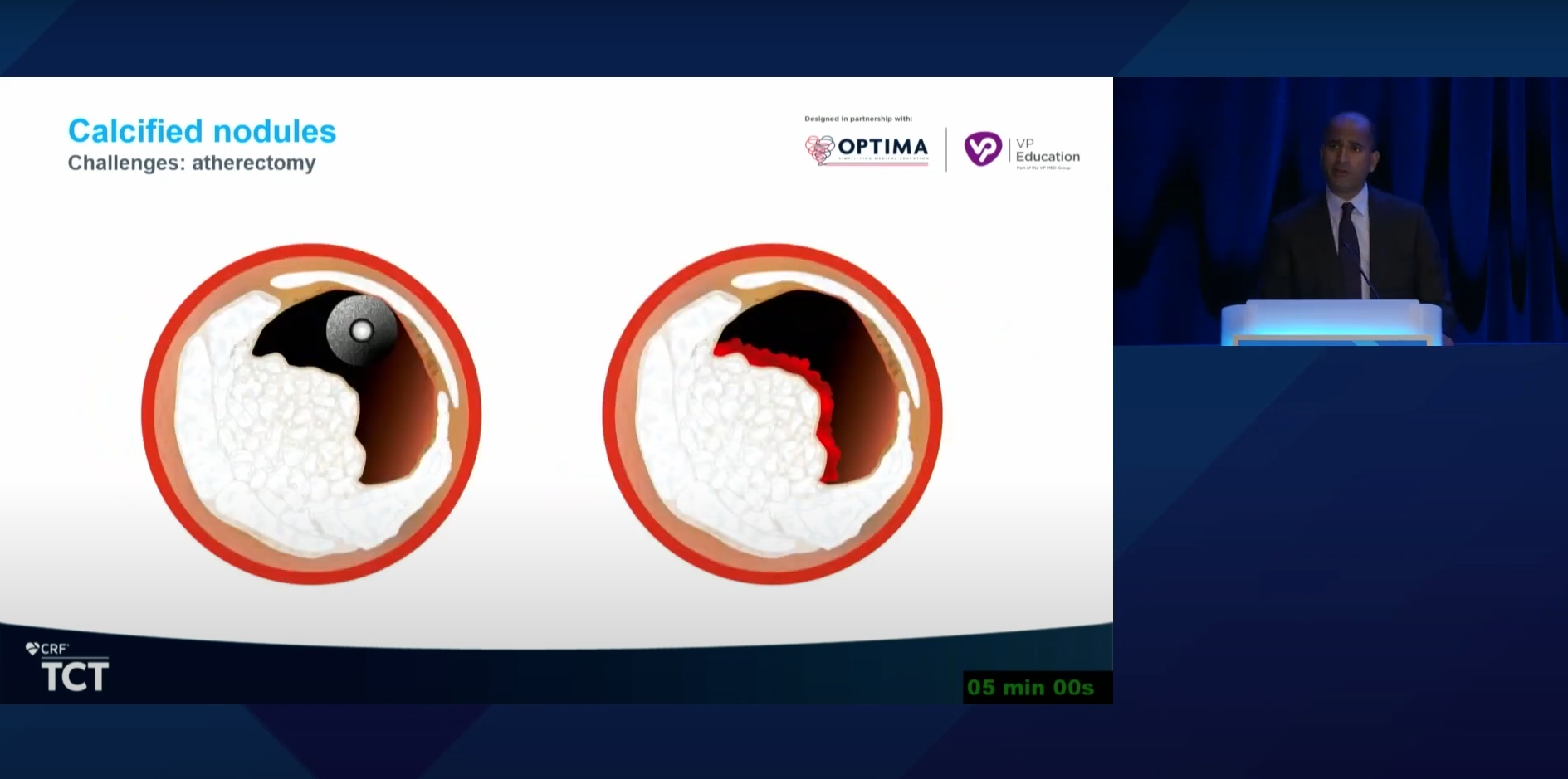
Shockwave IVL Provides Powerful Advantages When Treating Nodular Calcium
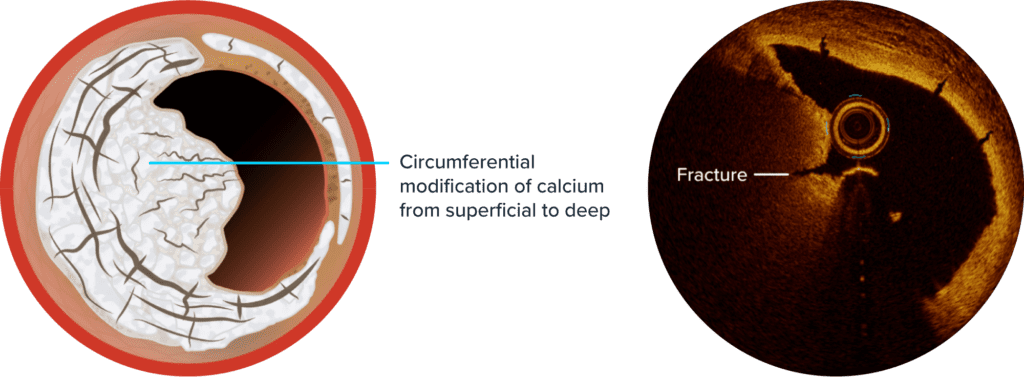
Traditional treatment methods such as balloon and atherectomy therapies have limitations when treating the unique pathologies associated with calcific nodules. Shockwave IVL’s unique mechanism of action (MOA) allows it to overcome these challenges. The sonic pressure waves created during Shockwave IVL therapy create a localized energy field effect which travels through soft vascular tissue to provide circumferential modification of both superficial and deep calcium.
OTHER THERAPIES:
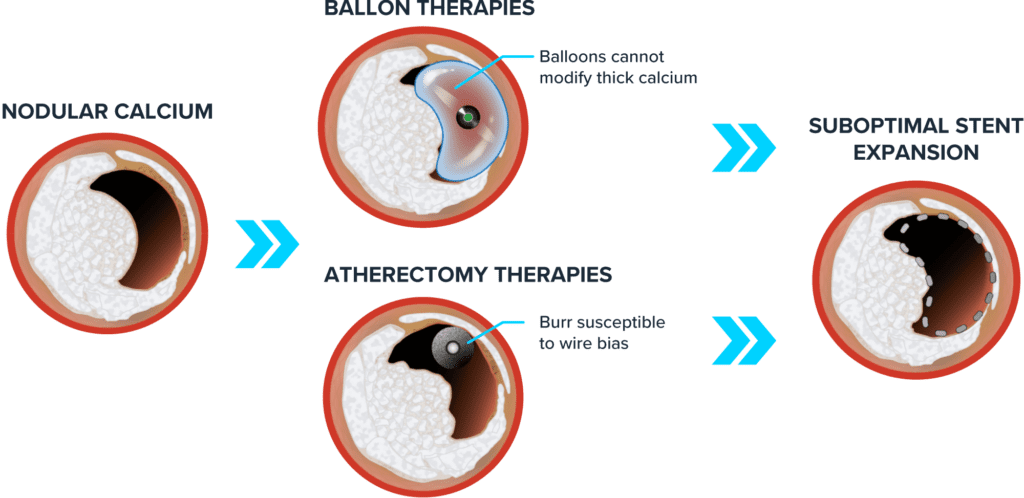
SHOCKWAVE IVL THERAPY:
| Lesion Effect | Balloon-Based Therapies | Atherectomy | Shockwave IVL |
| Not dependent on hydrostatic force | – | + + | + + |
| Selectively targets calcium | – | + + | + + |
| Able to modify deep calcium | + | – | + + |
| Independent of wire bias | + + | – | + + |
| Independent of lumen size | + + | – | + + |
Very favorable: ++
Neutral: +
Not favorable: –
NODULES TREATED WITH ATHERECTOMY RESULT IN WORSE LONG-TERM OUTCOMES

Morofuji T, et al. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021 Jan 1;97(1):10-19.
Shockwave IVL in Lesions with Calcified Nodules
POOLED DATA FROM THE DISRUPT CAD I-IV STUDIES
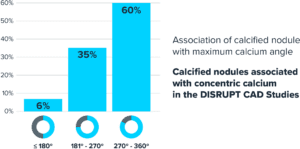
SPL 68507 Dispelling the Nodular Myths. Shockwave Medical 2023. Z. Ali TCT 2021.
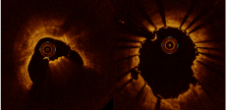
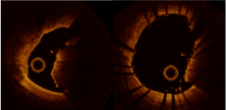
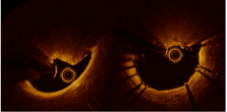
OCT Images Show Patterns of Stent Expansion post-IVL in Nodular Calcium
Shockwave IVL acoustic shock waves may affect calcium deep to the calcified nodules, allowing for concentric stent expansion in 77% of calcified nodular lesions.
-

Concentric expansion:
34% deformed eruptive calcified nodule -

Concentric expansion:
43% deformed nodule calcification -

Eccentric expansion*:
23% non-deformed nodular calcification
*Large MSA ensure good clinical outcomes despite eccentric stent expansion
OCT IMAGES OF IVL SHOW CONCENTRIC STENT EXPANSION WITH DEFORMED ERUPTIVE CALCIFIED NODULES
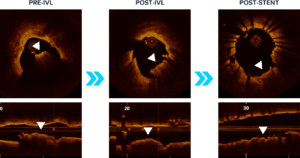
Moderated Poster, TCT 121: Intravascular Lithotripsy is Effective in the Treatment Calcified Nodules: Patient-level Pooled Analysis From the Disrupt CAD OCT Sub-studies, Ziad A. Ali, TCT 2021. Z. Ali et al JACC Int 2023.
OCT IMAGES OF SHOCKWAVE IVL SHOW CONCENTRIC STENT EXPANSION WITH DEFORMED NODULAR CALCIFICATION
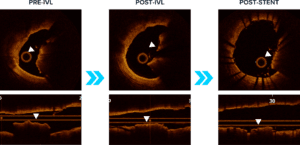
Moderated Poster, TCT 121: Intravascular Lithotripsy is Effective in the Treatment Calcified Nodules: Patient-level Pooled Analysis From the Disrupt CAD OCT Sub-studies, Ziad A. Ali, TCT 2021. Z. Ali et al JACC Int 2023.
OCT IMAGES OF SHOCKWAVE IVL SHOW ECCENTRIC STENT EXPANSION WITH NON-DEFORMED NODULAR CALCIFICATION

Moderated Poster, TCT 121: Intravascular Lithotripsy is Effective in the Treatment Calcified Nodules: Patient-level Pooled Analysis From the Disrupt CAD OCT Sub-studies, Ziad A. Ali, TCT 2021. Z. Ali et al JACC Int 2023.
Shockwave IVL is Consistent in Lesions With and Without Calcific Nodules
Consistent minimal stent area and stent expansion post-Shockwave IVL and stenting despite the presence of nodular calcium.
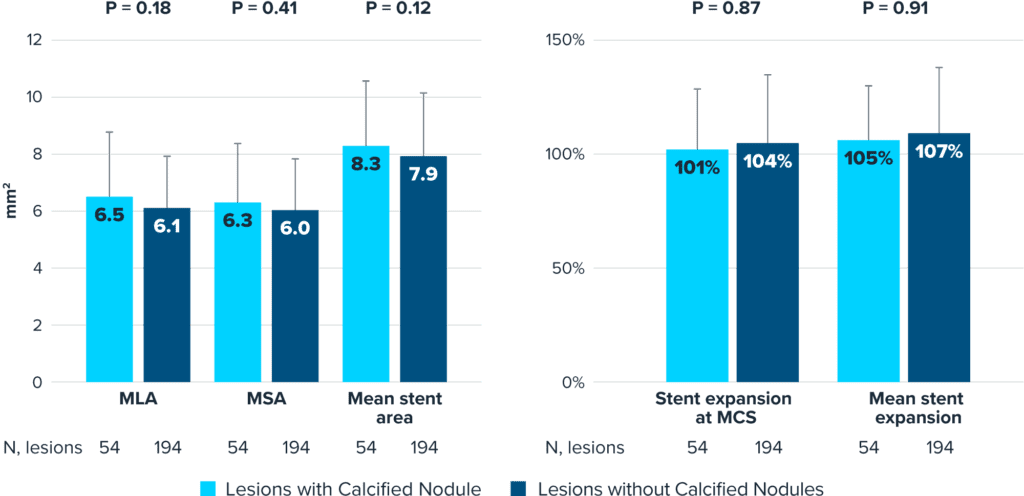
Pooled data from DISRUPT CAD I-IV OCT sub-studies; MLA, minimum lumen area; MSA, minimum stent area; and MCS, maximum calcium site.
Ali Z.A. Patient-pooled analysis of DISRUPT CAD OCT sub-studies (Conference presentation). TCT 2021 Orlando, FL, USA.
2-YEAR OUTCOMES
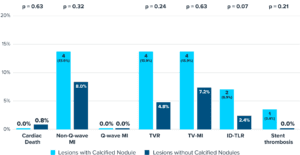
*N=1 ST event at POD 22
Shlofmitz, R., (2023, Feb 25-28) The impact of calcified nodules on 2-year clinical outcomes. CRT Annual Meeting, Washington, DC
Shockwave IVL in Calcific Nodules: Good Initial Insights But Still More to Learn

Review the full nodular OCT presentation at 30 days and two years:
What’s Next
More data are needed on nodules in larger, real-world cohorts across all calcium arcs, and the role of combination therapy (i.e. atherectomy + Shockwave IVL) in order to determine the optimal nodular strategy.